Come on folks, it's time to wake up to the real root causes of our problems!
Ascorbic Acid Deficiency as a Root Cause of Cardiopulmonary Pathology in Long COVID and Long VAXX
The Invisible Scorbutic Storm: Ascorbic Acid Deficiency as a Root Cause of Cardiopulmonary Pathology in Long COVID
A groundbreaking study by Trivieri et al. (2025) identified a high prevalence of persistent cardiopulmonary abnormalities in Long COVID (LC) and possible Long Vaxx patients using PET/MRI and dual-energy CT (DECT). Here I critically examine those findings through the lens of micronutrient biochemistry—specifically chronic ascorbic acid (vitamin C) insufficiency. From pulmonary perfusion defects to vascular inflammation and myocarditis, a coherent pathophysiological thread emerges: the protracted and often overlooked consequences of vitamin C depletion during and after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination with or without adverse reactions. Persistent oxidative stress, immune dysregulation, and collagen dysfunction—all hallmark features of subclinical scurvy—are key drivers of LC/LV pathology. The omission of vitamin C status in current diagnostic and treatment models represents a significant blind spot in both prevention and rehabilitation of these patients. Please not where I refer to LC patients I also include the possibility of LV patients.
1. Introduction
Long COVID has emerged as a global health challenge, with millions of individuals suffering from symptoms months to years after initial SARS-CoV-2 infection. These symptoms are frequently cardiopulmonary in nature, ranging from fatigue and dyspnea to myocarditis and valvular disease. The study by Trivieri et al. (J Nucl Med, July 2025) offers a robust imaging-based profile of these persistent abnormalities. Yet despite the detailed diagnostic insights, the root biochemical cause of these chronic conditions remains largely unexamined in the mainstream literature. I present a focused analysis of the imaging and biomarker findings in the Trivieri study and integrate them into a unified hypothesis grounded in clinical micronutrient pathology—specifically, vitamin C deficiency.
2. Summary of Findings from the Trivieri Study
The study enrolled 98 Long COVID patients with persistent cardiopulmonary symptoms 9–12 months post-infection, and 9 matched controls. Major findings included:
PET/MRI abnormalities in 57% of LC patients:
Myocardial inflammation (24%)
Pericardial inflammation (22%)
Periannular (mitral valve region) uptake (11%)
Vascular inflammation, notably in the pulmonary artery (30%)
DECT abnormalities in 90%:
Pulmonary infiltrates (67%)
Perfusion defects (59%)
Plasma protein imbalances:
↑ IL-2, IL-7, IL-10, IL-17A
↓ IFN-γ, TNF-α, VEGF-A
Clinical follow-up (3.8 years):
15% had cardiovascular events
9% developed heart failure
2% developed mitral valve disease
1 patient developed pulmonary hypertension
3. Pathophysiological Interpretation Through the Lens of Vitamin C Deficiency
A. Pulmonary Dysfunction and Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C is essential for lung tissue maintenance and pulmonary vascular integrity. Its antioxidant role mitigates alveolar oxidative stress, enhances epithelial barrier function, and regulates surfactant secretion. The widespread DECT findings—pulmonary infiltrates and perfusion defects—correlate with the known consequences of ascorbate deficiency:
Increased capillary fragility
Reduced nitric oxide bioavailability
Impaired alveolar gas exchange
B. Myocardial and Pericardial Inflammation
Vitamin C:
Downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α)
Supports cardiac collagen synthesis and scar repair
Prevents microvascular ischaemia via endothelial protection
In the study, myocarditis and pericarditis were common. These pathologies are known sequelae of scurvy-like states in which oxidative stress is unchecked and collagen synthesis is impaired, leading to inflammation, oedema, and even arrhythmogenic remodelling.
C. Periannular and Valvular Disease
The detection of periannular 18F-FDG uptake (mitral valve region) in 11% of subjects mirrors subclinical valvular inflammation akin to that seen in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Vitamin C is central to:
Collagen cross-linking (via proline/lysine hydroxylation)
Valvular integrity
Suppression of autoimmunity through modulation of Th17 and Treg pathways
Suboptimal ascorbate levels can accelerate valvular deterioration by compromising extracellular matrix stability and enabling persistent inflammation.
D. Vascular Inflammation and Pulmonary Hypertension
PET/MRI data showing vascular uptake in 30% of subjects, especially in pulmonary arteries, is concerning. Vitamin C is known to:
Prevent endothelial dysfunction
Inhibit VCAM-1 expression
Maintain capillary tone and elasticity
A deficiency can lead to vascular remodeling and, ultimately, pulmonary hypertension—as observed in at least one patient in the study.
E. Immune Dysregulation
The cytokine profile in LC patients (↑ IL-17A, IL-10; ↓ IFN-γ, TNF-α) suggests Th17 dominance with suppressed antiviral Th1 responses. This immune imbalance is well-documented in scorbutic states. Vitamin C:
Promotes IFN-γ synthesis and NK cell activity
Suppresses IL-17A-driven chronic inflammation
Restores balanced macrophage polarization
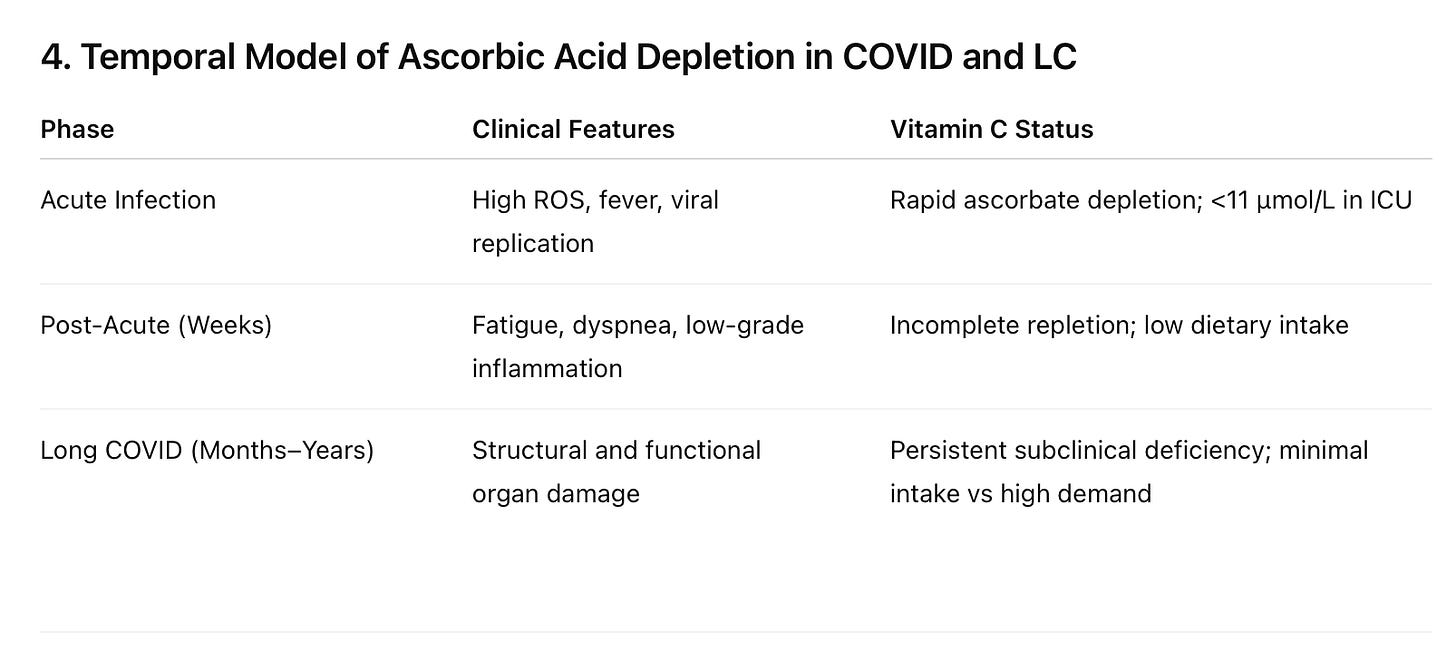
5. Conclusion
The cardiopulmonary findings in Long COVID mirror the consequences of a long-neglected, reversible condition: subclinical scurvy. The absence of vitamin C assessment in this population constitutes a critical oversight in both diagnosis and care. Integrating high-dose ascorbic acid into LC/LV treatment and prevention strategies warrants urgent clinical investigation. Clinical experience with severely ill pulmonary patients over the past 5 decades supports the use of High Dose Intravenous Vitamin C (HDIVC) at the earliest possible stages of an infectious disease to prevent such catastrophic clinical outcomes.
6. Recommendations
Include plasma and leukocyte vitamin C level monitoring in all LC/LV studies.
Initiate controlled trials using high-dose intravenous and oral vitamin C.
Educate clinicians on the signs of functional hypovitaminosis C in post-viral syndromes.




Good analysis. By the way, it’s probable that “long Covid” is actually “long vax” ie, covering up injury and death from the “vaccines” by shifting attention to the purported deadliness of “Covid”
You might be interested in Lactuca virosa metabolites (Lactucin and Lactucopicrin) - and their role in IL-6 and TNF-\alpha down regulation. I've been doing a bit of meta-analysis on metabolites that are active in this space. [Also on Benzimidazoles, anti-parasitic action]. I've looked into the Lactuca metabolites as I wanted to investigate them for anti-parasitic/protozoal properties - (which are exhibited via a tubulin interaction)... I also took a look at tonic + [cranberry|lemon]:-) I never get sick, you see. I did not get injected. I use L. virosa as an anti-inflammatory - occasionally as a decoction, but also with boutique lettuce (in my sammitches - which I make myself:-D) The key to health is nutrition.